

It wasn’t by accident that the original GSX-R750 redefined the high-performance Supersport and shocked the motorcycle world when it was introduced in 1985.
It was a product of integrated design, a talented group of Suzuki chassis, engine and electrical engineers making history by working together to build a more compact and lighter 750cm 3 Supersport.
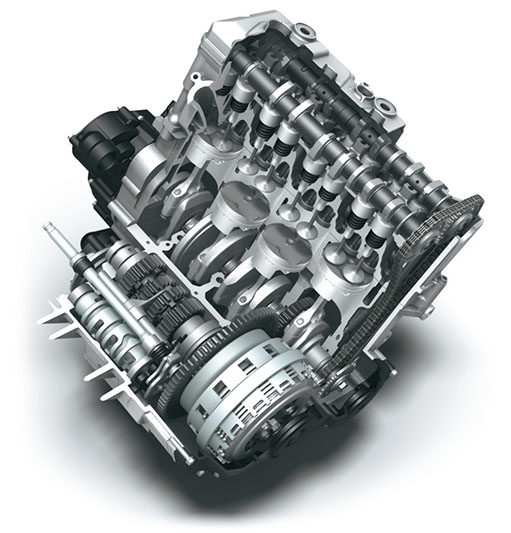
Combustion efficiency is a measure of how completely an engine burns its fuel.
Better combustion efficiency can increase power and torque output across the rpm range; improve throttle response, acceleration and fuel mileage; and reduce emissions.
Mechanical efficiency is a measure of how much of the power and torque produced by an engine actually reaches the rear wheel.
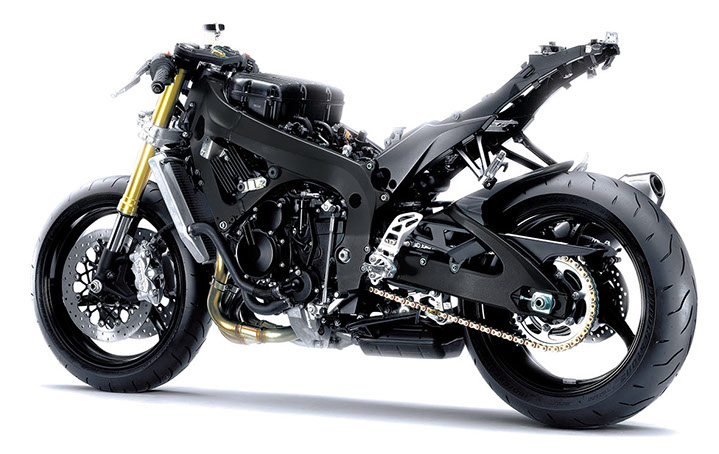
The GSX-R750 and GSX-R600 models both feature completely chassis designs, each based on a more compact, lighter twin-spar aluminum frame with a 15 mm shorter wheelbase.
The GSX-R750’s wheelbase is 1,390 mm while the GSX-R600’s wheelbase measures 1,385 mm.
The overall combined weight of the transmission gearsets is reduced. The race-proven ramp-and-cam design of the back-torque-limiting clutch reduces pressure on the plates during deceleration, producing smoother downshifting and corner entry and allowing the track rider to concentrate on braking and cornering.
The crankcases carry a six-speed close-ratio transmission with vertically staggered shafts, to reduce overall engine length, and a back-torque-limiting clutch.
The GSX-R600’s revised close-ratio six-speed transmission features a taller first-gear ratio and shorter ratios for 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 6th gear, making it easier for a racer to get a good start and also improving straight-line acceleration and drive out of corners.
For the first time, both the Suzuki GSX-R750 and the Suzuki GSX-R600 come with the revolutionary, race-developed Showa Big Piston Front-fork (BPF) inverted front suspension system. Conventional inverted front forks use a cartridge assembly that fits inside the fork leg on each side and typically incorporates a 20 mm piston to control damping.
The four-into-one stainless-steel exhaust system features four individual head pipes and a single collector. The mid-pipe located between the collector and the under-engine exhaust chamber carries a Suzuki Exhaust Tuning (SET) servo-controlled butterfly valve to match exhaust system back-pressure to engine rpm, throttle position and gear position, maximizing torque and improving throttle response, especially in the low-to-mid rpm range. The exhaust chamber leads to stainless-steel S-bend pipe and a titanium muffler shaped and positioned to enhance cornering clearance and improve aerodynamics. A reduction in pipe wall thickness and a smaller, more efficient exhaust chamber and muffler combine to make the GSX-R750 system 1,100 grams lighter and the GSX-R600 system 1,700 grams lighter.
A slightly larger-diameter radiator fan mounted on the efficient, trapezoidal, curved radiator turns on and off based on coolant temperature and improves cooling performance.
Both GSX-Rs feature a repositioned engine management computer (also known as the Engine Control Module, or ECM) to allow the wiring harness to be simplified and made lighter.
The ECM operates a state-of-the-art Suzuki Dual Throttle Valve (SDTV) closed-loop fuel injection system, an advanced ignition system and several emission control systems, producing better throttle response, smoother power delivery, improved mileage and reduced emissions.
With an unmatched combination of excellent throttle response, linear power delivery, strong braking, confident handling and class-leading power-to-weight ratio, it was the closest a mass-production four-stroke, four-cylinder streetbike had ever come to being a racebike with lights.
Reducing mechanical losses by minimizing internal engine friction, reducing the weight of reciprocating internal parts and relieving crankcase pressure can increase mechanical efficiency, putting more of an engine’s output to use actually moving and accelerating the motorcycle and also improving fuel mileage and reducing emissions.
For both models, the shorter wheelbase better centers the combined machine/rider mass between the wheels, improving racetrack cornering and also shortening the reach between the seat and the handlebars. The shorter reach and slightly wider handlebar angle make it easier for the rider to reposition their weight while on the racetrack and also improve comfort on longer highway rides.
The advanced BPF design eliminates the separate internal cartridge assembly inserted into each fork leg and instead uses a single, 37.6 mm piston riding against the inside wall of the 41 mm inner fork tube. The larger BPF piston and valving shims produce more effective, more accurate and more linear damping performance. The more controlled compression damping is especially noticeable during hard braking and at corner entry, delivering better feedback to the rider.
OWN THE RACETRACK
EFFICIENCY BY DESIGN
A LIGHTER, MORE COMPACT CHASSIS
ENGINE DESIGN
ENGINE MANAGEMENT
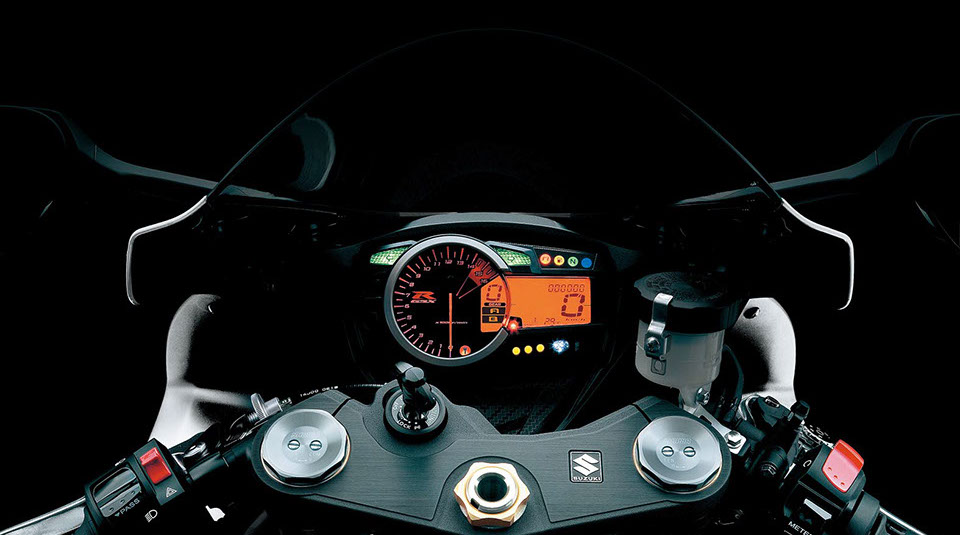
SOPHISTICATED INSTRUMENTATION
RACING SUSPENSION

The GSX-R600 uses lighter, more durable forged pistons designed with the same Finite Element Method (FEM) and fatigue analysis technology used to develop MotoGP racing engines. Shorter and narrower skirts, narrower wrist pin bosses and shorter wrist pins help make each piston assembly 78 grams lighter. The lighter piston assembly translates into less reciprocating weight, reducing mechanical losses while improving throttle response, acceleration and engine output reaching the rear wheel.
Each GSX-R750 cylinder’s two intake valves measure 29.0 mm in diameter while the two exhaust valves measure 23.0 mm in diameter. The redesigned intake valves are each 0.6 gram lighter thanks to the stronger titanium alloy and reshaped valve heads.
The GSX-R600’s titanium intake valves measure 27.2 mm in diameter, while the titanium exhaust valves measure 22.0 mm in diameter. The camshaft profiles produce a more aggressive valve-lift curve to improve throttle response, mid-rpm torque and peak engine output while also preventing valve spring surge at high rpm. The cam profiles were designed using advanced technology developed by Suzuki engineers working on ultra-high-revving MotoGP racing engines. The GSX-R600 is the first production Suzuki motorcycle to benefit from this proven MotoGP racing technology.
On the racetrack, that translates to better drives out of corners and higher top speeds. On the street, it means that the GSX-R600 doesn’t have to be revved as much to accelerate briskly away from a stop.





RIDER-SELECTABLE MAPPING
The Suzuki Drive Mode Selector (SDMS) system built into the ECM allows the rider to use a button mounted on the left handlebar switch module to select one of two engine control maps, regulating the fuel injection, secondary throttle valve and ignition systems. The two maps are designated A and B, with Map A delivering full power and acceleration and Map B producing more moderate acceleration.
The SDMS system allows the rider to select a map to suit various riding conditions and personal preference on the road, for example choosing one map for highway cruising and the other map for tight country roads.
More compact and lighter instrument cluster installed on the GSX-R750 and the GSX-R600 is standard equipped with a built-in lap timer/stopwatch and a programmable, sequential engine rpm indicator system. Both those features can be useful at track days or during club-racing weekends.
For some riders, The Original GSX-R’s combination
of 750cm 3 power in a compact,nimble,
600cm 3 - size chassis is what a Supersport should be.
If that rider is you, the GSX-R750 is ready. For other riders,
the ideal Supersport is The Top Performer in the 600cm 3 class.
If you are that rider, your GSX-R600 is waiting.
See your dealer now, and start making your own history.
RADIAL-MOUNT BREMBO
The Suzuki GSX-R750 and GSX-R600 both come with 310 mm fully-floating front brake discs and radial-mount, four-piston Brembo monoblock calipers. The 32 mm caliper pistons are staggered to promote even pad wear, the trailing pistons offset relative to the pad centerline. The monoblock design of the calipers makes them lighter, and their more rigid construction and increased piston area improve braking performance by providing the rider with more consistent power and better feel at the lever.
THE ORIGINAL GSX-R, AND THE 600cm 3TOP PERFORMER
Transmission
Front suspension
Rear suspension
Front brake
Rear brake
Front tire size
Rear tire size
Ignition system
Fuel tank capacity
Oil capacity (Overhaul)
Transmission
Front suspension
Rear suspension
Front brake
Rear brake
Front tire size
Rear tire size
Ignition system
Fuel tank capacity
Oil capacity (Overhaul)
6-speed constant mesh
Inverted telescopic, coil spring,
oil damped
Link type, coil spring, oil damped
Disc, twin
Disc
120/70ZR17M/C (58W), tubeless
180/55ZR17M/C (73W), tubeless
Electronic ignition (transistorized)
17.0 L (4.5/3.7 US/Imp gal)
2.9 L (3.1/2.6 US/lmp qt)
*North American Spec. shown
*North American Spec. shown
6-speed constant mesh
Inverted telescopic, coil spring,
oil damped
Link type, coil spring, oil damped
Disc, twin
Disc
120/70ZR17M/C (58W), tubeless
180/55ZR17M/C (73W), tubeless
Electronic ignition (transistorized)
17.0 L (4.5/3.7 US/Imp gal)
2.9 L (3.1/2.6 US/lmp qt)
Specifications
2,030 mm (79.9 in)
710 mm (28.0 in)
1,135 mm (44.7 in)
1,390 mm (54.7 in)
130 mm (5.1 in)
810 mm (31.9 in)
190 kg (419 lbs)
4-stroke, 4-cylinder, liquid-cooled, DOHC
70.0 mm x 48.7 mm (2.8 in x 1.9 in)
750 cm3 (45.8 cu. in)
12.5 : 1
2,030 mm (79.9 in)
710 mm (28.0 in)
1,135 mm (44.7 in)
1,385 mm (54.5 in)
130 mm (5.1 in)
810 mm (31.9 in)
187 kg (412 lbs)
4-stroke, 4-cylinder, liquid-cooled, DOHC
67.0 mm x 42.5 mm (2.6 in x 1.7 in)
599 cm3 (36.5 cu. in)
12.9 : 1
Overall length
Overall width
Overall height
Wheelbase
Ground clearance
Seat height
Curb mass
Engine type
Bore × Stroke
Displacement
Compression ratio
Overall length
Overall width
Overall height
Wheelbase
Ground clearance
Seat height
Curb mass
Engine type
Bore × Stroke
Displacement
Compression ratio



Metallic Triton Blue / Metallic Mystic Silver (GUL)
Metallic Oort Gray No.3 (QEB)
Pearl Brilliant White (YUH)

Metallic Triton Blue / Metallic Mystic Silver (GUL)

Pearl Brilliant White (YUH)

Metallic Mat Black No.2 (YKV)
© Suzuki Motor Corporation, . All rights reserved.


